Financial giant Visa has proposed a method that allows users to pay blockchain gas fees using their Visa cards.
Blockchain transactions, especially on platforms like Ethereum, require users to pay gas fees. These fees are essentially the cost of processing a transaction on the blockchain. Traditionally, these fees are paid using the native cryptocurrency of the platform, such as Ether for Ethereum. However, Visa’s new approach aims to simplify this process for users who might not have ready access to these cryptocurrencies or prefer to use their credit cards.
According to Visa’s recent thought leadership paper, here is how this would work:
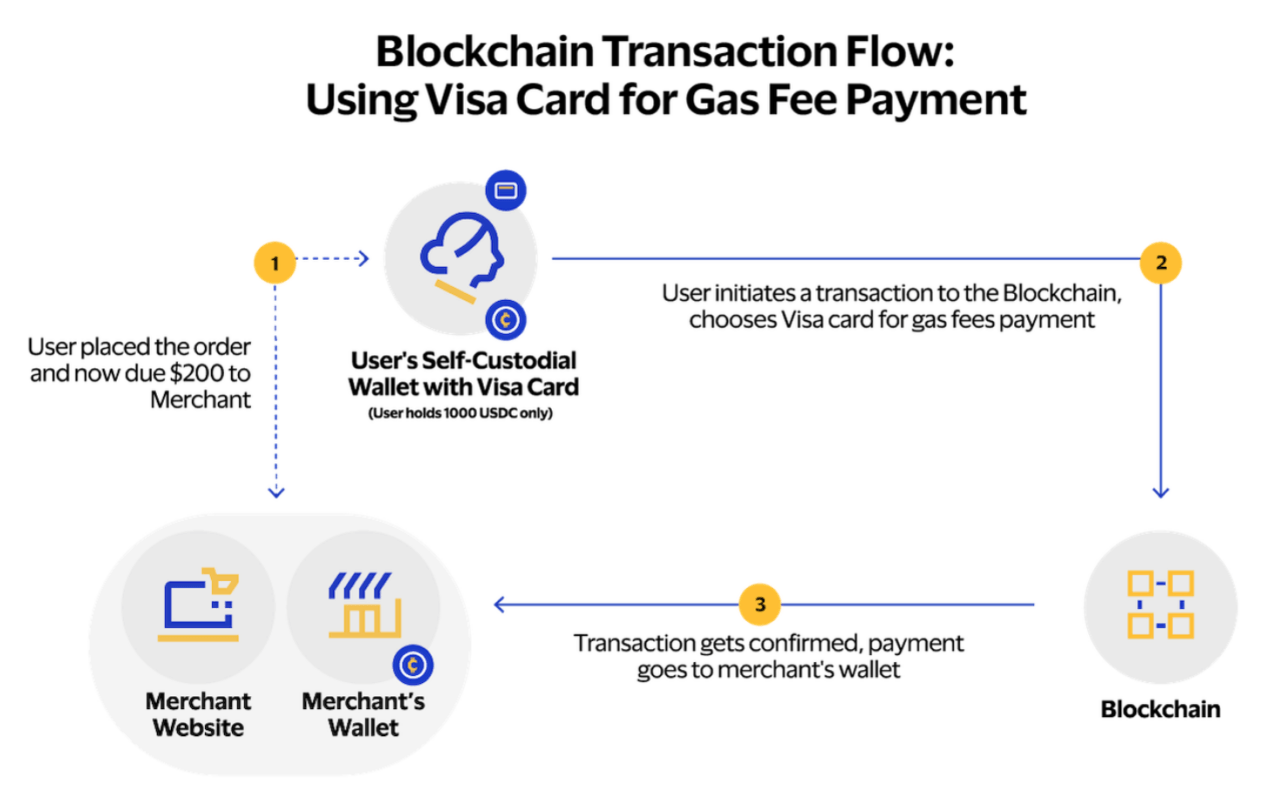
- Initiating a Blockchain Operation: When a user wants to conduct an action on the blockchain, their digital wallet creates a “User Operation” request. This request contains details about the intended action and the maximum cost associated with it, which includes the gas fees.
- Payment through Visa: Instead of immediately sending this request to the blockchain, the digital wallet forwards the User Operation and the user’s Visa card details to a specialized web service. This service calculates the fiat currency equivalent of the gas fee. Using Visa’s Cybersource payment solution, the service processes the card payment. Cybersource, a part of Visa’s ecosystem, provides the necessary tools for merchants to accept digital payments seamlessly.
- Digital Signature Creation: Once the payment is approved, the web service generates a digital signature for the User Operation data, which includes the action details and gas fee information. This signature is time-bound, ensuring that users cannot exploit potential price fluctuations in Ethereum or other tokens. The digital signature, along with its valid time window, is then sent back to the user’s wallet.
- Sending to the Blockchain: The wallet appends the received digital signature and the paymaster contract’s on-chain address to the User Operation. With all components in place, the wallet can now sign the operation and forward it to the blockchain.
- Blockchain Verification: On the blockchain, the paymaster contract, which adheres to the ERC-4337 standard, reviews the User Operation data. If the data, including the digital signature from the web service, is valid, the paymaster contract approves the transaction. However, if there’s any discrepancy, such as an incorrect signature or an expired time window, the contract will flag an error and won’t cover the gas fees. A correct signature indicates that the web service has received the card payment, allowing the paymaster contract to cover the transaction’s processing cost.
Featured Image Credit: Photo / illustration by AgelessFinance via Pixabay